Unemployment Insurance in Macroeconomic Stabilization with Imperfect Expectations
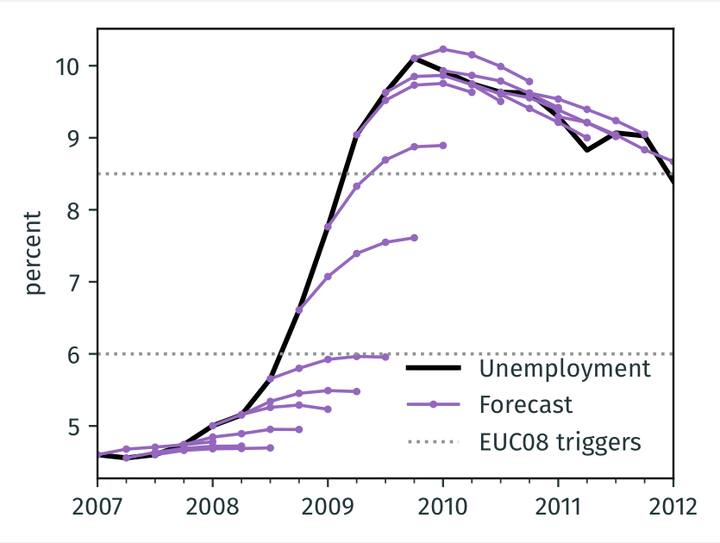 Unemployment Rate Forecast during the Great Recession
Unemployment Rate Forecast during the Great RecessionAbstract
We study the power of state-dependent unemployment insurance (UI) to stabilize short-run fluctuations, allowing for arbitrary deviations from full information and rational expectations. Expectations are critical because higher UI generosity raises consumption, to a large extent, by lowering precautionary savings. If UI generosity is indexed to the unemployment rate, households must forecast the unemployment rate to anticipate the policy stance. We estimate unemployment expectations in response to identified aggregate shocks. We quantify the consequences of these imperfect expectations through the lens of a Heterogeneous Agent New Keynesian model. First, we work directly with the estimated forecast errors. Our methodological contribution is to use the non-parametric history of forecast errors and forecast revisions to solve dynamic decisions of optimizing agents. By doing so, we sidestep the need to choose a particular model of belief formation. The estimated model implies that imperfect anticipation substantially affects the stimulative power of UI extensions. Second, we compare alternative ways of implementing UI policies. To run counterfactuals, we estimate a structural model of belief formation. We show that a combination of noisy information and diagnostic expectations fits the data best among a large set of popular alternatives. A UI extension that is announced directly is more stimulative in the very short run than one that is indexed to the unemployment rate.