
The Macroeconomic Effects of Excess Savings
We study excess savings decumulation in a quantitative HANK model.
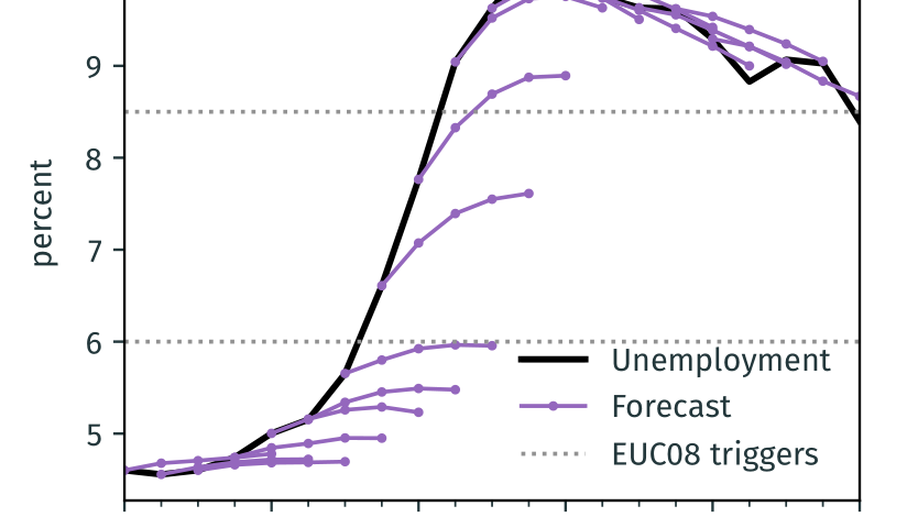
Unemployment Insurance in Macroeconomic Stabilization with Imperfect Expectations
We study the power of state-dependent unemployment insurance (UI) to stabilize short-run fluctuations, allowing for arbitrary deviations from full information and rational expectations.
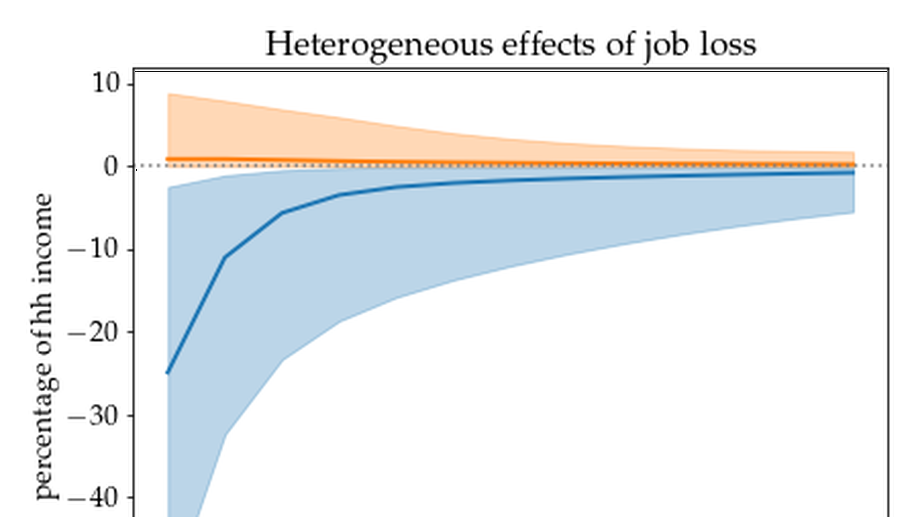
Spousal Insurance and the Amplification of Business Cycles
I develop a Heterogeneous Agent New Keynesian model with dual-earner households that offers new insights into the role of spousal labor supply at both the micro and the macro levels. The model matches existing microeconomic evidence on the response of household earnings and consumption to the job loss of the primary earner. Specifically, it implies that the average job loser suffers large income loss, only a small fraction of which is compensated by the spouse. Nevertheless, the model reveals that this low average spousal earnings response to job loss masks substantial benefits for consumption smoothing. Looking at the average income replaced by the spouse is misleading for two reasons: heterogeneity and interdependence between different margins of the adjustment. At the macro level, countercyclical labor supply of secondary earners can stabilize aggregate demand but it also crowds out primary earners searching for jobs. The model implies that the aggregate demand channel dominates, and spousal insurance is an effective automatic stabilizer.
MPCs, MPEs, and Multipliers: A Trilemma for New Keynesian Models
We show that New Keynesian models with frictionless labor supply face a challenge: given standard parameters, they cannot simultaneously match plausible estimates of marginal propensities to consume (MPCs), marginal propensities to earn (MPEs), and fiscal multipliers. A HANK model with sticky wages provides a solution to this trilemma.
Using the Sequence-Space Jacobian to Solve and Estimate Heterogeneous-Agent Models
We propose a general and highly efficient method for solving and estimating general equilibrium heterogeneous-agent models with aggregate shocks in discrete time.
